 Did you know that you have an endocannabinoid system?
Did you know that you have an endocannabinoid system?
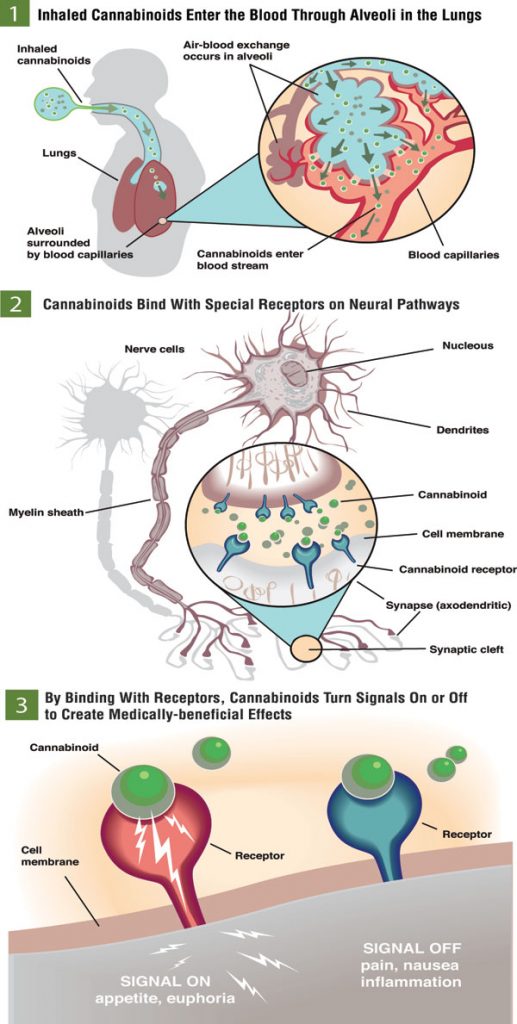
The endocannabinoid system was initially discovered in the late 1980s when scientist studied how THC and other cannabinoids interact. Cannabis can function efficiently in mammal’s due to a series of receptors in the pathways of the brain called the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Cannabinoids bind with the endocannabinoid
receptors, creating medical effects
by suppressing signals
such as pain, nausea and depression
while boosting appetite and euphoria.
It was discovered that humans are designed to interact with cannabinoids through the ECS which consist of CB1 and CB2 receptors. Cannabinoids and terpenes are delivered to the bloodstream either through the lungs (when inhaled), the digestive system (when consumed) or the skin (when applied topically). From the blood stream, cannabinoids become available to the central nervous system through the CB1 receptors and the immune system through CB2 receptors.
These receptors influence the flow of chemical signals to the brain and digestive system. Cannabinoids bind with the endocannabinoid receptors, creating medical effects by suppressing signals such as pain, nausea and depression while boosting appetite and euphoria. Cannabis use effects the neurotransmitter GABA by blocking it. The result is increasing dopamine levels which GABA normally inhibits or regulates. Dopamine offers a mood shift of reward for the brain that is released with sex, exercise, appetite, learning, sleep, movement and mood.
Cannabis effects the cannabinoid receptors, namely CB1 and CB2 that mimic a naturally created endogenous molecule, anandamide. Anandamide is an Omega 6 fatty acid that regulates appetite, cognition, emotion, memory, mood and pain. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and other cannabinoids found in cannabis can affect anandamide and therefore effect the endocannabinoid central nervous system.
The most exciting and promising lines of research into the role of the endocannabinoid system is in the regulation of inflammation and the immune system. Clinical evidence has shown the effectiveness of endocannabinoids on treating epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, muscle spasms and other neuromuscular system disorders.



